At the End, Offering Not a Cure but Comfort
Anemona Hartocollis, New York Times (August 19, 2009)
I started and re-started this post on American Health Care reform several times. To watch America’s current Health Care debate (such as it is…) makes me all the happier that I now live in the UK and am covered by the National Health Service. I have no problems with the NHS and I am glad that it exists.

One part of the NHS that impresses me most is its National End of Life Care Programme. The EOLC Programme’s mission statement provides a succinct mandate:
OUR AIM: To improve the quality of care at the end of life for all patients and enable more patients to live and die in the place of their choice.
What I think is fundamentally important about this NHS program is that it acknowledges the obvious: people die. Indeed, the program was explicitly created to embrace death so that the dying process is made as comfortable as possible for UK residents.

Herein lies one of the key reasons that I think the American Health Care reform debate is failing: Serious discussions about death, dying, and mortality have been jettisoned. What America needs more than ever, right now, is a National Conversation about dying because until that occurs, health care reform will continue to ignore that one part of human biology that we all share: Death.
And yet, paradoxically, it would seem that this kind of conversation is going on all the time.
The New York Times article at the top offers a lengthy and important discussion on End of Life Care in American hospitals. And NYTimes Health columnist Jane Brody offered this recent piece: End-of-Life Issues Need to Be Addressed.
President Obama made it clear in May that he was interested in a National Conversation about End of Life Care in a lengthy New York Times Magazine interview about the economy.
It is a long(ish) interview, so if you click here you can skip to the bit on Obama’s Grandmother and how her death informed his own thinking about End of Life decisions.

The problem, of course, is that people rarely talk to their family members about death. To bring home this point, the August 7, 2005 New York Times Magazine featured this article: Will We Ever Arrive at the Good Death?
Here is the key quote from that article:
As J. Donald Schumacher, president of the National Hospice and Palliative Care Organization, said last April to the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, “Americans are more likely to talk to their children about safe sex and drugs than to their terminally ill parents about choices in care as they near life’s final stages.”
Let me be clear that I think that President Obama is delving into an extremely urgent topic but, ironically, he is not the first modern American president to discuss end of life decision making. Oh no. Not by a long shot.
Some of the first presidential statements on death involved Ronald Reagan. In the early 1980’s, President Reagan received a series of reports on death and dying from some totally forgotten (but important) bioethics commissions:
- Defining Death: Medical, Legal and Ethical Issues in the Determination of Death (July 9, 1981)
- Deciding to Forego Life-Sustaining Treatment: Ethical, Medical, and Legal Issues in Treatment Decisions (March 21, 1983)
So, in a way, President Obama is attempting to carry out a project begun by President Reagan and is actually acting very Reaganesque. But I digress…
For me, the key reason President Obama has seen his health care debate derailed is that he dared to embrace death. Or, at least, to suggest that end of life care is something that needs to be discussed (on the local and national level) since individuals need to be clear in their own heads about how they want to die.
And since President Obama is involving himself in this debate, it means that the head of the nation is suddenly speaking out about death and dying. As a result, Obama is acknowledging a much more profound dilemma for modern America: the nation-state (as in America) usually ignores death at all costs.
At a certain point, the nation can do absolutely nothing about death and instead it focuses on mortality. Death is utterly ignored by the nation because it represents that one, final act that an individual can choose and that beyond a certain point-in-time no life will return. President Obama isn’t anywhere near making statements about who lives and who dies. But he is making it clear that death is inevitable. (I am unfairly paraphrasing Michel Foucault’s comments from his Society Must Be Defended lectures, p. 248).
That alone, I think, is causing some of the biggest problems.

All of this is to say, that American health care reform begins and ends with death. And until those discussions occur, America will continue with its current system.
If you’re interested in making sure that your own end of life requests are followed, then use this information offered by Jane Brody of the New York Times.
To help people make sound health care decisions and get the care they would want for themselves or their family members as life draws to a close, the National Institute on Aging has produced a comprehensive 68-page booklet, “End-of-Life: Helping With Comfort and Care.” Individual free copies can be obtained through the institute’s Web site, www.nia.nih.gov, or by calling 800-222-2225.
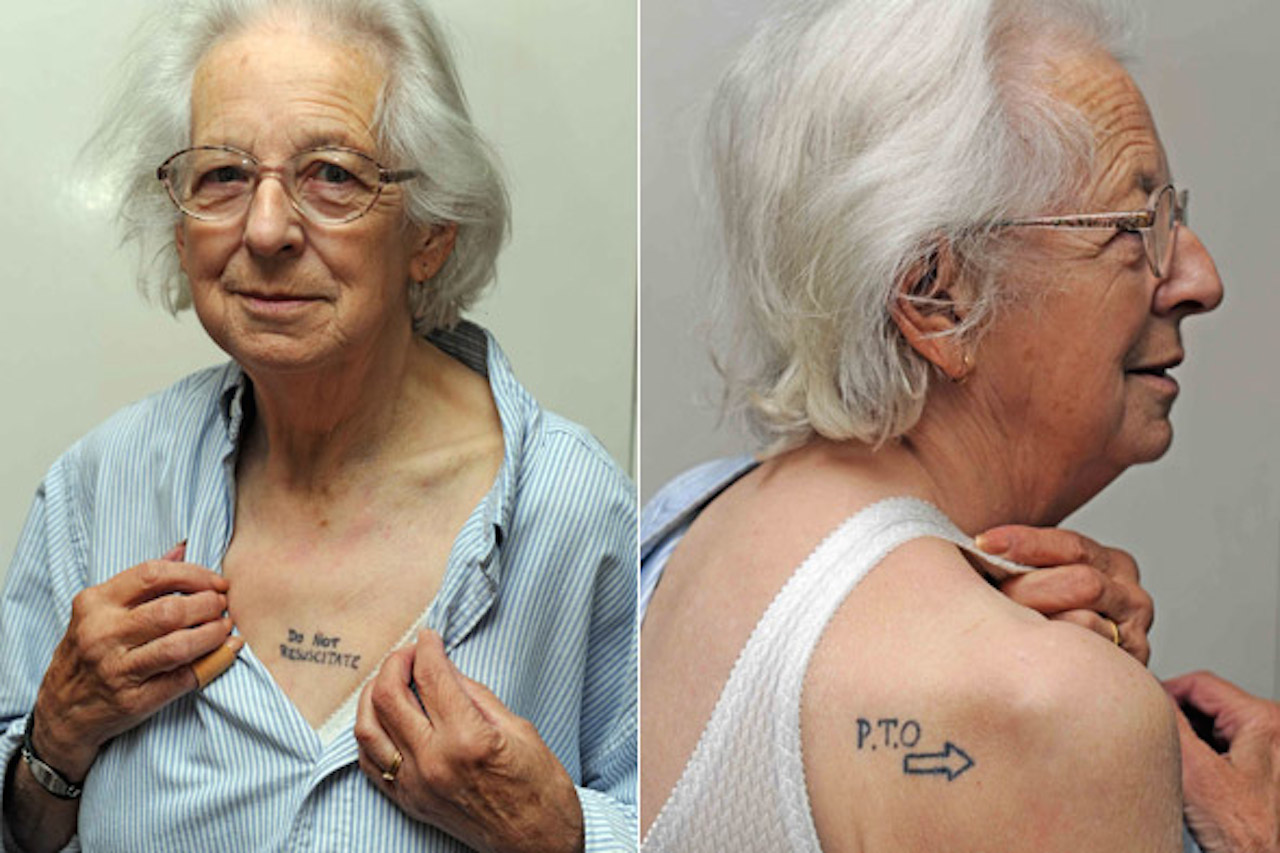
 ave been intrigued for some time by the arguments Kurzweil and others make, especially when it comes to lifespan. A number of Singularity believers talk about 700 year lifespans and/or the outright elimination of death. I don’t ever discount these ideas out of hand. It is truly impossible to predict where human biology will end up fifty or one hundred years from now. So, I actually think that eliminating death or greatly expanding lifespan might be possible.
ave been intrigued for some time by the arguments Kurzweil and others make, especially when it comes to lifespan. A number of Singularity believers talk about 700 year lifespans and/or the outright elimination of death. I don’t ever discount these ideas out of hand. It is truly impossible to predict where human biology will end up fifty or one hundred years from now. So, I actually think that eliminating death or greatly expanding lifespan might be possible.




